Power grid studies
IEC 60287 Cable Analysis
Background
In high-voltage networks, significant power flows through cables over long distances. Their heating, due to Joule losses in the conductors, plays a key role when it comes to their sizing. Proximity effects due to neighbouring conduits, asymmetry effects and the influence of environmental conditions must also be taken into account.
Complying with the thermal limits is essential to:
- Ensure the cable’s lifespan by preventing insulation degradation;
- Guarantee installation safety (avoiding fires and protection tripping).
The IEC 60287 standard is used for the thermal sizing of electrical cables, particularly in medium- and high-voltage (HV) applications, when installation methods and operating frequencies do not allow the use of NFC 13-200 standard.
Requirement
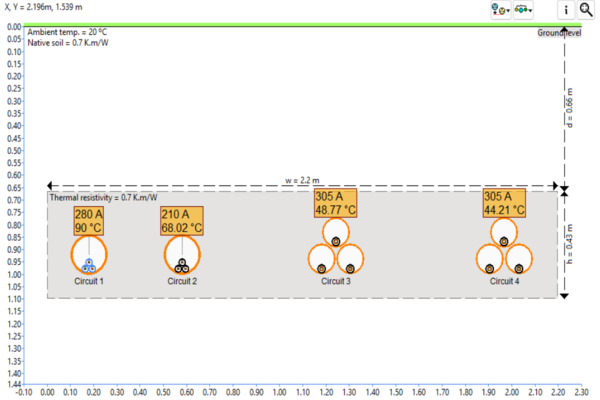
It is necessary to determine the maximum permissible current of an HV cable based on:
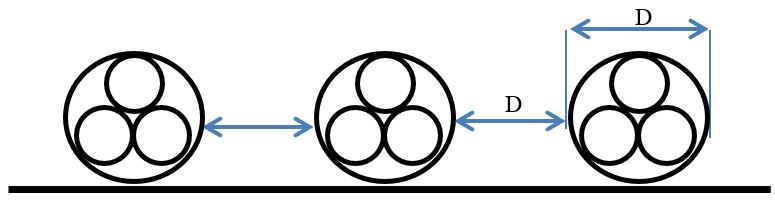
- The geometry of its cross-section (various layers of insulation and materials);
- Its environment (soil, air, conduit, ducts, etc.);
- Installation conditions (depth, soil thermal resistivity, proximity with heat sources or other cables, etc.).
Principle :
CAPSIM performs modelling of cables and their installation method using a dedicated software, allowing to perform thermal calculations in accordance with the IEC 60287 standard. It is possible to compute the skin temperature (core–insulation interface) for a given current or to determine the maximum permissible current.
This modelling considers the materials from which the different cable layers are made and the installation method. It is also possible to consider the specific harmonic spectrum of currents caused by the presence of a variable speed drive, or to take into account cyclic power flow effects (for example for projects involving solar energy or batteries).
Results
Applying the IEC 60287 standard enables to:
- Determine the permissible current at the maximum acceptable temperature of the cable’s insulation;
- Optimise economic sizing (avoiding under- or oversizing).